📖 Hobby BASIC Quick Guide
A simple but surprisingly capable BASIC interpreter, developed in 32-bit x86 assembly.
A brief tour of some of the features and capabilities of the language.
🎯 35,000+ lines of polished game code and examples
🚀 Continuously evolving since 2015
Key Features:
- BASIC-like syntax with rich collection of specialized commands
- Full keyboard & mouse input in console
- ANSI-encoded graphics support
- UDP networking functions
- Standalone pseudo-executables
- Windows XP/7/10/11 compatible
- DRAW - ANSI drawing tool fully written in Hobby BASIC
- FPU string math & Win32 API support
- Super Tiny BASIC interpreter included with full source code
My goal has always been to create a simple, user-friendly language designed for game development within the Windows console—and I believe it's progressing quite well!
🎥 Watch the full video tour on YouTube to see Hobby BASIC in action.
✅ Conditionals in Hobby BASIC
1. IF...THEN...ELSE Statement
The IF...THEN...ELSE structure is used to control program flow based on conditions.
Example 1: Simple IF Statement
IF SCORE >= 50
PRINT "You passed!"
ENDIFExample 2: IF...ELSEIF...ELSE
IF (GRADE$ = "A" AND ATTENDANCE >= 90) OR AGE > 18
PRINT "Great job!"
ELSEIF (GRADE$ = "B" OR AGE <= 18) AND ATTENDANCE >= 50
PRINT "Good effort!"
ELSE
PRINT "Keep improving!"
ENDIFExample 3: Nested IF Statements
IF AGE >= 18
IF COUNTRY$ = "USA" THEN PRINT "You can vote."
ELSE
PRINT "You are too young to vote."
ENDIFExample 4: Single-line IF with THEN
IF BALANCE < 0 THEN PRINT "Your account is overdrawn!" ELSE PRINT "Balance OK."Example 5: IF without ELSE
IF LOGIN$ = "admin"
PRINT "Access granted."
ENDIF2. IIF Function
The IIF function evaluates a condition and returns one of two values.
Example 6: Basic IIF Usage
STATUS$ = IIF(SCORE >= 60, "Pass", "Fail")Example 7: Numeric IIF Example
DISCOUNT = IIF(QUANTITY > 10, 1, 0)Example 8: String Assignment with IIF
COUNTRY$ = IIF(COUNTRY$ = "", "Unknown", COUNTRY$)3. SELECT...CASE...ENDSEL Statement
The SELECT...CASE structure simplifies multiple condition checks.
Example 9: Simple SELECT...CASE
INPUT "Enter day of week (1-7): ", DAY
SELECT CASE DAY
CASE IS 1 :
PRINT "Monday"
BREAK
CASE IS 2 :
PRINT "Tuesday"
BREAK
CASE IS 3 :
PRINT "Wednesday"
BREAK
CASE IS 4 :
PRINT "Thursday"
BREAK
CASE IS 5 :
PRINT "Friday"
BREAK
CASE IS 6,7 :
PRINT "Weekend"
BREAK
CASE IS :
PRINT "Invalid day"
ENDSELExample 10: SELECT...CASE without parameter
SELECT CASE
CASE TEMP > 30 :
PRINT "Hot"
BREAK
CASE TEMP >= 20 AND TEMP <= 30 :
PRINT "Warm"
BREAK
CASE TEMP < 20 :
PRINT "Cold"
BREAK
ENDSEL✅ Loops and Control Statements
1. FOR...NEXT Loop
The FOR...NEXT loop in Hobby BASIC is used to repeat a block of code for a specific number of times.
Example 1: Basic FOR Loop with PASS
FOR I = 1 TO 5
IF I = 3 THEN PASS
PRINT I
NEXT IExpected Output: 1 2 4 5
2. DO...UNTIL Loop
The DO...UNTIL loop executes a block of code repeatedly until a condition is met.
Example 2: DO Loop with PASS
I = 0
DO
I = I + 1
IF I = 2 THEN PASS
PRINT I
UNTIL I = 4Expected Output: 1 3 4
3. WHILE...ENDW Loop
The WHILE...ENDW loop repeats a block of code as long as the condition is true.
✍️ Note: Hobby BASIC uses ENDW instead of WEND.
Example 3: WHILE Loop
I = 1
WHILE I <= 5
PRINT I
I = I + 1
ENDWExpected Output: 1 2 3 4 5
4. PASS Statement
The PASS statement is used to skip the current iteration of a loop. It is similar to the continue statement in C.
Example 4: Simple PASS Usage
FOR I = 1 TO 3
PASS
PRINT I
NEXT IExpected Output: (Nothing printed)
5. BREAK Statement
The BREAK statement is used to exit a loop prematurely when a certain condition is met.
Example 5: Simple BREAK Usage
FOR I = 1 TO 9
IF I = 5 THEN BREAK
PRINT I
NEXTExpected Output: 1 2 3 4
6. Nested Loops with BREAK and PASS
You can also use BREAK and PASS inside nested loops to control the flow.
Example 6: Nested Loops with PASS
FOR I = 1 TO 3
FOR J = 1 TO 3
IF J = 2 THEN PASS
PRINT "I=", I, " J=", J
NEXT J
NEXT IExpected Output:
I=1 J=1
I=1 J=3
I=2 J=1
I=2 J=3
I=3 J=1
I=3 J=37. Complex Example: Search for Prime Numbers
In this example, we will search for prime numbers up to a limit using BREAK and PASS.
Example 7: Search for Prime Numbers
LIMIT = 20
PRINT "Prime numbers up to ", LIMIT
PRINT 2, " ";
FOR NUM = 3 TO LIMIT STEP 2
ISPRIME = 1
I = 3
WHILE I * I <= NUM
IF NUM % I = 0
ISPRIME = 0
BREAK
ENDIF
I = I + 2
ENDW
IF ISPRIME THEN PRINT NUM;
NEXTExpected Output: 2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19
✅ Functions in Hobby BASIC
1. Validated User Input (1–100)
This function prompts for numeric input and checks for valid range and characters.
Example: getValidatedNumber Function
sub getValidatedNumber()
while 1
! prompt for input
INPUT "Please enter a number (from 1 to 100):", num$
! remove whitespace
num$ = TRIM(0, num$)
! check if input is empty
if not LEN(num$)
pass
! check for invalid characters (only digits allowed)
elseif not INSET(num$, "0123456789")
PRINT "Invalid characters in string, please try again."
! convert to number and check range
else
num = VAL(num$)
if num < 1 or num > 100
PRINT "Invalid value, please try again."
else
rets num ! return valid number
endif
endif
endw
ends
! call the function and display the result
number = getValidatedNumber()
PRINT "You entered:", number✍️ Note: The INPUT command needs an active screen buffer to work.
view 11
screen 80, 30, 30002. Searching for a Value in an Array
This function searches for a target value in an array and returns its index if found.
Example: searchArray Function
sub searchArray(arr[], target)
! search for the target value in the array
arr[].FIND target
rets V0 ! return the index (0 if not found)
ends
! create an array with 50 random numbers (1–50)
dim numbers[50].RND 50
searchValue = 10
! call the function and store the result
index = searchArray(numbers[], searchValue)
! check if the value was found
if index <> 0
PRINT "Value ", searchValue, " found at position ", index - 1
else
PRINT "Value ", searchValue, " not found in the array"
endif3. Loading File Content into an Array
This function loads lines of text from a file into an array.
Example: loadFileIntoArray Function
sub loadFileIntoArray(filePath$, lines$[])
! check if file exists (SIZE returns -1 if not found)
if SIZE(filePath$) = -1 then rets -1
! load file contents into string array
lines$[].FILE filePath$
rets V0 ! return number of lines loaded
ends
! create a string array with 100 empty slots
dim fileBuffer$[100].ZERO
! load the file into the array and get the line count
lineCount = loadFileIntoArray("Licence.txt", byref fileBuffer$[])
! check for file not found error
if lineCount = -1
PRINT "Error: File not found"
end
endif
! print each line of the loaded file
for i = 0 to lineCount - 1
PRINT fileBuffer$[i]
next4. Swapping Two Values
This function swaps two values using a temporary variable.
Example: swapValues Function
sub swapValues(x, y)
! store the value of x in a temporary variable
local temp = x
! swap the values
x = y
y = temp
ends
firstValue = 5
secondValue = 10
! swap the two values using byref parameters
swapValues(byref firstValue, byref secondValue)
! print the swapped values
PRINT "After swapping: ", firstValue, " and ", secondValue5. Checking if a String is a Palindrome
This function checks if a string is a palindrome (reads the same forwards and backwards).
Example: checkPalindrome Function
sub checkPalindrome(inputString$)
! declare local variables
local reversedString$
local cleanedInput$
! remove spaces from the input
cleanedInput$ = REPLACE(inputString$, " ", "")
! reverse the cleaned string
reversedString$ = REVERSE(cleanedInput$)
! compare the reversed and original (case-insensitive)
if UCASE(reversedString$) = UCASE(cleanedInput$)
rets "The string is a palindrome!"
else
rets "The string is not a palindrome!"
endif
ends
! call the function and display the result
result$ = checkPalindrome("Rotator")
PRINT result$✅ The Stack in Hobby BASIC
In Hobby BASIC, the stack operates in a LIFO (Last In, First Out) manner and consists of 262,140 double words. You can manipulate it using the basic PUSH and POP commands or directly through the stack[] array.
✍️ Note: The stack[] array and the internal stack are the same. Any operation on stack[] directly affects the stack. However, commands like FILL, SHUFFLE, SORT, etc., do not update the internal stack pointer, so use them with care.
Example: Basic PUSH and POP
push 100
push 'A'
pop xThis sends 100 and the ASCII of 'A' to the stack, and retrieves 'A' into x.
Example: Multiple PUSH and Top Check
push 1, 2, 3, 'A'
top = PEEK(10) ! Get top of the stack
print CHR(stack[top - 1]) ! Prints 'A'
pop 4 ! pop 4 timesSorting the Stack
x = 0
dim stack[10] ! reinitialize stack with 10 elements
times 10 push x++ ! pushes 0..9 onto the stack
stack[].SORTD ! now stack[] = [9, 8, …, 0]
for i = 0 to 9
print stack[i]
nextExpected Output: 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 (Descending order)
Value Replacement
dim stack[5]
push 10, 20, 30, 20, 40
stack[].REPLACE 20, 99
times 5 pop x : print xExpected Output: 40 99 30 99 10
Extra: Stack SHUFFLE
dim stack[5]
push 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
stack[].SHUFFLE
times 5 pop x : print x✍️ Note: SHUFFLE randomly shuffles stack values. The result will vary.
Handling the Circular Stack
The Hobby BASIC stack is circular. When it becomes full, new values start replacing older ones from the beginning of the array.
Example: Circular Stack Behavior
dim stack[5]
push 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
push 6, 7
top = PEEK(10)
arr_size = 5
for i = 0 to arr_size - 1
print stack[i]
nextExpected Output: 6 7 3 4 5
Reading Top to Bottom with Wrap-around
🔄 Always use mod to handle circular wrap‑around when reading from top to bottom.for i = 1 to 5
idx = (top - i + arr_size) mod arr_size
print stack[idx]
nextExpected Output: 7 6 5 4 3
Alternative: Simple POP
times 5 pop x : print xExpected Output: 7 6 5 4 3
The stack in Hobby BASIC is a powerful tool. Its circular nature makes it highly efficient not only for simple PUSH and POP operations but also for advanced manipulations like sorting, shuffling, and value replacements using the stack[] array.
✅ Drawing Tool Guide
Introduction
This drawing tool is developed in Hobby BASIC and designed specifically for use within the Hobby BASIC environment. DRAW can load, create, edit, and save ANSI images.
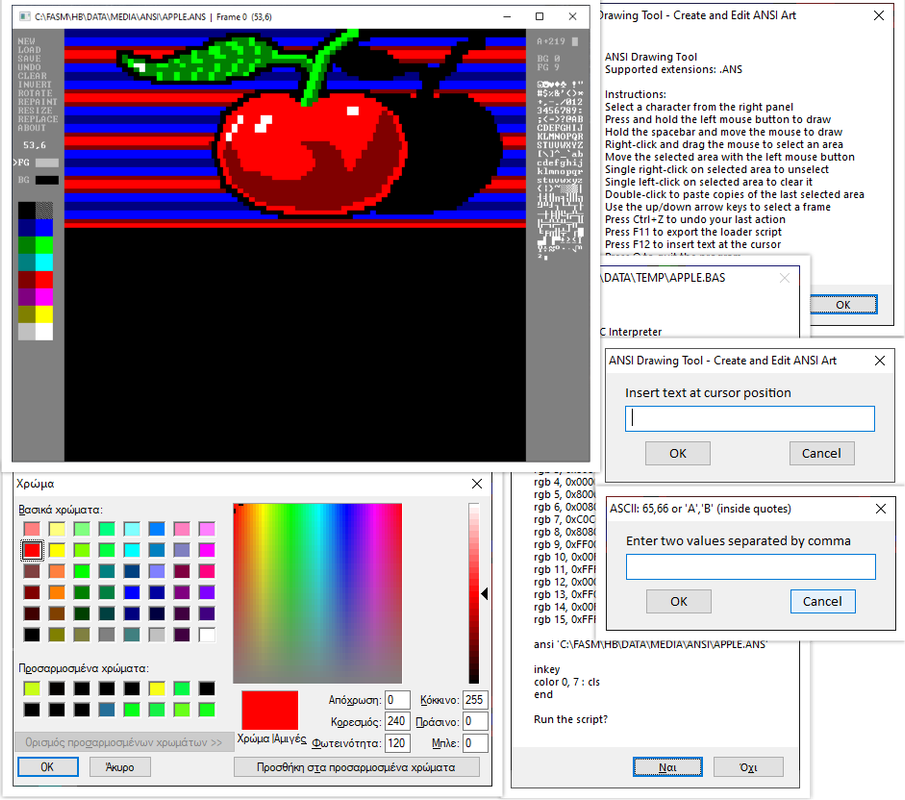
Basic Controls
- Press and hold the left mouse button to draw.
- Hold the spacebar and move the mouse to draw.
- Hold the right mouse button and drag to select an area on the screen.
- Move a selected area by clicking and dragging it with the left mouse button.
- Right-click on a selected area to deselect it.
- Left-click on a selected area to delete it.
- Double right-click to paste copies of the last selected area anywhere on the screen or in a different frame.
- Use the up/down arrow keys to select a frame.
- Right-click on the color picker to open the color dialog box.
- Press
Ctrl + Zto undo the last action. - Press
F11to export the loader script. - Press
F12to insert text at the cursor. - Press
Qto quit the program.
The Attributes Picker
Click on the BG or FG labels to select background or foreground color.
Then choose one of the 16 available colors from the color picker.
💡 Right-click on the labels to swap the foreground and background colors.
If an area is selected, the color swap will apply to that area automatically.
✍️ Note: This method overrides color number 8 (GRAY) as it is used for temporary storage.
The Color Dialog Box
Right-click on the color picker to open the color dialog box.
Any change you make to one of the 16 basic colors in the console will affect the entire DRAW window.
Remember, DRAW itself is a console window made with Hobby BASIC.
🎨 About Color Schemes
When you save an image in DRAW, the program automatically stores the associated color scheme in the DATA\TEMP folder. The scheme is saved as a plain text file (.TXT) with the same name as your image. To load this scheme, use Option 3 from the main menu.
Function Keys
- F1 – Start a new drawing
- F2 – Open a drawing (.ANS file)
- F3 – Save the drawing (.ANS file)
- F4 – Undo last action (Ctrl + Z)
- F5 – Clear the selected area
- F6 – Invert the selected area
- F7 – Rotate the selected area
- F8 – Repaint the selected area (change BG color to FG color)
- F9 – Resize the selected area (double its size)
- F10 – Replace characters in the selected area
📌 Windows 10 & 11 Compatibility
For the program to function correctly, enable the Use Legacy Console option:
- Right-click the app title bar and select Properties.
- Enable Use Legacy Console.
- Restart the console.
✅ Creating Snapshots
Introduction
The DRAW program, Hobby BASIC's drawing tool, offers three options when starting:
- Default mode: Font 8x12 with a canvas size of 80x50 cells.
- Alternative mode: Font 8x8 with a canvas size of 80x75 cells.
- Load RGB color scheme: Loads a color configuration from the DATA\TEMP folder.
⚠️ Note: Options 1 and 2 define the font and canvas size used during your drawing session. Make sure to choose the correct mode when loading an image you previously created, to match its original dimensions.
Loading an ANSI Image
For example, if we save an image named TEST.ANS in the DATA\MEDIA\ANSI\ folder, we can load it as follows:
! ROWS = 80
! COLS = 25
screen 80, 50, 0
cls
ansi PATH("DATA\MEDIA\ANSI\TEST.ANS")
inkeyThe critical setting here is ROWS, which must be 80.
Saving a Portion of an Image
The following code creates a new ANSI image, TEST1.ANS, with a size of 40x25 from the original TEST.ANS file.
screen 80, 50, 0
cls
ansi PATH("DATA\MEDIA\ANSI\TEST.ANS")
ansi 0, 0, 40, 25, PATH("DATA\MEDIA\ANSI\TEST1.ANS")
inkeyLoading the Cropped Image
To load TEST1.ANS, the console window must match the image size:
screen 40, 25, 0
cls
ansi PATH("DATA\MEDIA\ANSI\TEST1.ANS")
inkeyℹ️ Using SNAP for More Flexibility
SNAP loads a snapshot file at position x, y, or saves a rectangular area of the screen to a file. Snapshot files require the .HB extension. SNAP allows us to load an image of any size into a console window of any dimensions (as long as it fits within the window).
✍️ Note: Since version 2.4.5, the SNAP command now automatically includes the console's 16-color palette. This means:
🔹Perfect color reproduction every time
🔹Backward compatible with older .HB files
Creating and Loading a Snapshot
To load TEST.ANS and create a snapshot named TEST.HB with a size of 40x25, use the following code:
screen 80, 50, 0
cls
ansi PATH("DATA\MEDIA\ANSI\TEST.ANS")
snap 0, 0, 40, 25, PATH("DATA\SNAP\TEST.HB")
inkeyNow, we can load this snapshot at any position within the console window:
screen 80, 50, 0
cls
snap 10, 10, PATH("DATA\SNAP\TEST.HB")
inkey✅ Hobby BASIC - Try These
📌 Built-in Functions Overview
Useful one-liners and built-in functions:
print ABS(-10) ! 10
print RND()%100 ! random number 0-99
print STR(25) + " years" ! "25 years"
print FORMAT(1, 23456) ! "22,9 KB"
print PAD("42", '0', 5) ! "00042"
print EXTRACT("abc123!@#", 0) ! "123"👉 Use PAUSE or INKEY to prevent the window from closing.
🧵 Strings in Hobby BASIC
String manipulation with built-ins:
a$ = "Hello World"
print LEFT(a$, 5) ! "Hello"
print RIGHT(a$, 5) ! "World"
print REVERSE(a$) ! "dlroW olleH"
a$(0) = 'h' ! Change first char (0-based)🧮 Arrays (1D & 2D)
Working with arrays and array functions:
dim nums[5] = 5, 3, 1, 4, 2
nums[].SORTA
nums[].PRINT 3
nums[].REPLACE 3, 99
nums[].PRINT 3
! 2D example:
dim matrix[2, 2] = 1, 2, 3, 4
print matrix[0, 0], matrix[1, 1] ! prints 1 4Example: Load file into string array and display lines.
dim lines$[100].FILE PATH("LICENCE.TXT")
lineCount = V0
for idx = 0 to lineCount - 1
print lines$[idx]
next🎨 Console Drawing & Screen Tools
Manipulate screen output using built-in commands:
cls
color 1, 14
print "Yellow on Blue!"
paint 0, 0, 80, 25, 'Α', 1
invert 10, 10, 15, 5
redraw 10, 10, 15, 5, 'Α', '-'You can redefine any of the 16 default console colors using the RGB command:
rgb 1, 0x00A5FF ! Set color #1 to orange
color 0, 1
print "Now using custom orange text!"You can also use the alternate format with separate RGB components:
rgb 1, 255, 165, 0 ! equivalent to rgb 1, 0x00A5FF (note: color is in 0xBBGGRR format)This allows for personalized color schemes inside your apps or tools built with Hobby BASIC.
📂 File & Snapshot Utilities
Working with files and snapshots:
! Load text from file into array
dim lines$[]
lines$[].FILE "LICENCE.TXT"
for i = 0 to SIZE(lines$[]) - 1
print lines$[i]
next
! Save a portion of screen
snap 0, 0, 40, 15, PATH("DATA\SNAP\TEST.HB")
! Load the snapshot
snap 10, 10, PATH("DATA\SNAP\TEST.HB")🔁 Mini Lab: Digital Clock
Create a simple digital clock:
while 1
print at 0, 0, LEFT(PATH(10), 8) ! system time
wait 1000
endw🗺️ Mini Mini Lab: Three Points
TYPE is a user-defined structure that can hold variables or strings.
! Define a Coord structure for 3 points
type Coord (x, y) 3
! Assign coordinates to each point
Coord:[0].x = 10 : Coord:[0].y = 5 ! Point 0 at (10,5)
Coord:[1].x = 20 : Coord:[1].y = 15 ! Point 1 at (20,15)
Coord:[2].x = 30 : Coord:[2].y = 25 ! Point 2 at (30,25)
! Loop through and print each point
for i = 0 to 2
print "Point ", i, ": (", Coord:[i].x, ", ", Coord:[i].y, ")"
next
⌨️ Keyboard Input
Wait for a key press and display the key code:
LOOP#
inkey
! V0 = Keycode
! V1 = SHIFT, ALT, CTRL, etc.
! V2 = F1..F12, INS, DEL, HOME, Arrows Keys
print "Key:", V0, " Mod:", V1, " Extra:", V2
if V0 = 13 then print "Enter was pressed"
if V0 = 27 then end ! Exit with Esc
goto LOOP
🖱️ Mouse Tracking
Track mouse position and button state:
while 1
mouse
! V0 = mouse x
! V1 = mouse y
! V2 = button: 1 left, 2 right, 4 double-click
print "X:", V0, " Y:", V1, " Btn:", V2
if V2 = 2 then print "Right click!"
if V2 = 1 then break ! Left click to exit
wait 1
endw
✍️ Note: Mouse input requires no screen buffer.
view 11
screen 80, 30, 0✅ Hobby BASIC - Advanced
⚙️ FIX and TIMES
FIX replaces code before execution, letting you use alternative keywords or rename commands.
TIMES is like a compact loop. It runs a single-line command multiple times using V3 as the counter.
wait1Sec fix wait 10
display fix print
times 100 display V3 : wait1SecWith the above fix, you can write display instead of print, or even use your native language!
📝 Full Wide & Greek-native support with fix command
Hobby BASIC is fully Wide-native, supporting Greek identifiers and keywords. To use Greek keywords in your code,
first declare them with the fix command, linking the Greek word to the corresponding English command.
For example:
! After these mappings, you can write your program using Greek commands directly
ΠΡΟΒΟΛΗ fix VIEW
ΟΘΟΝΗ fix SCREEN
ΧΡΩΜΑ fix COLOR
ΣΒΗΣΙΜΟ fix CLS
ΤΥΠΩΣΕ fix PRINT
ΠΑΥΣΗ fix PAUSE
ΑΡΧΗ#
ΠΡΟΒΟΛΗ 11
ΟΘΟΝΗ 80, 30, 1000
ΣΒΗΣΙΜΟ
ΧΡΩΜΑ 0, 7
ΤΥΠΩΣΕ "Υποστηρίζω Ελληνικά"
ΠΑΥΣΗAll source code, tokens, labels, and strings are handled as Wide, enabling case-sensitive Greek and Latin text everywhere.
✍️ Note: To display Greek characters correctly, Hobby BASIC requires a raster font that supports Wide glyphs.
🛠️ DEBUG() Window Examples
Use the DEBUG window to visualize variable contents in real time:
dim values[5] = 10, 20, 30, 40, 50
for i = 0 to 4
DEBUG(i, values[i]) ! show key-value pairs in debugger
next
Viewing output of an external command.
exec "tasklist", list$
debug(list$)This will show the list of running processes from the Windows tasklist command directly inside the DEBUG window.
🔗 Run Remote Scripts Anywhere
One of Hobby BASIC’s unique features is the ability to run remote .BAS scripts
directly from the command line, without needing to download them manually. Try the following in the command line and see what it does.
HB.EXE https://files.catbox.moe/ia9qt7.BASAlternatively, you can run remote scripts dynamically from within another .BAS program:
exec "run https://files.catbox.moe/ia9qt7.BAS"This command fetches the .BAS file from the specified URL, loads it into memory, and executes it in the console.
⚠️ Security Warning: Scripts from remote URLs run with full privileges. Only run code from trusted and verified sources.
🧮 Floating-Point Functions
Hobby BASIC supports optional floating-point math through external functions. All arguments and results are passed as strings, making it easy to use floats without affecting the integer core.
print FADD("3.14", "2.0") ! "5.14"
print FSUB("10", "2.5") ! "7.50"
print FMUL("3.0", "2.0") ! "6.00"
print FDIV("1.0", "0.0") ! "0.00"
! Using variables, strings, arrays, types
x$ = "3.14" : y = 2
dim a$[] = "1.5", "2.5"
type T (x$ = "3.5", y$ = "2.5")
print FADD(x$, y) ! "5.14"
print FADD(a$[0], a$[1]) ! "4.00"
print FMUL(T:[0].x$, T:[0].y$) ! "8.75"⭕ Drawing a circle in console using FPU string math and TIMES command.

▶ View source code
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! TIMES WITH FPU STRINGS
! Drawing a circle in console using FPU string math and TIMES command
! Note: TIMES uses backslash (\) as continuation character for multi-line blocks
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! Initialize display (font size 8x8)
title "FPU CIRCLE"
view 7
screen 40, 25, 0
cursor 0
color 0, 15
cls
times 360 \
! Calculate circle coordinates (360 degrees in radians)
a$ = FDIV(FMUL(V3,"6.28318"),"360.0") : \
x = VAL(FROUND(FADD("20.0",FMUL(FSIN(a$),"9.0")),"NEAREST")) : \
y = VAL(FROUND(FADD("12.0",FMUL(FCOS(a$),"9.0")),"NEAREST")) : \
if x >= 0 and x < 40 and y >= 0 and y < 25 then at x, y, "█"
! Clean exit
inkey
color 0, 7 : cls
view 11
end👉 Why strings?
Floating-point functions operate on string arguments to maintain compatibility with Hobby's integer-based architecture. This makes conversions explicit and avoids hidden side effects. It also keeps the system small, portable, and easy to debug. See the Hobby BASIC manual for more details about the floating-point set and how to use it effectively in your programs.
⚙️ Win32 Power with syscall
With Hobby BASIC you can call Windows API functions, unlocking features beyond standard BASIC —from message boxes to launching programs, querying system info, or even experimenting with simple GDI graphics in the console.
syscall "user32.dll", "MessageBoxW", 0, "Hello from BASIC!", "Title", 0APIs can also return values. For example, get system uptime in milliseconds:
syscall "kernel32.dll", "GetTickCount"
print "Milliseconds since boot: ", V0Or play a simple system beep using kernel32.dll:
syscall "kernel32.dll", "Beep", 750, 300Structures made of DWORD fields are supported by using arrays with
byref, letting you call functions such as GetWindowRect to retrieve window dimensions.
⚠️ Warning: Native API calls run with full privileges. Incorrect use may cause crashes. Use only documented functions and safe values!
📖 See the Hobby BASIC Manual for details and the EXAMPLES\API folder for samples.
🛠️ Super Tiny BASIC – Built with Hobby BASIC
Super Tiny BASIC is a minimal yet powerful ’80s-style BASIC interpreter written entirely in Hobby BASIC.
It supports single-letter variables (A–Z), single-line IF statements, structured loops (FOR/NEXT, WHILE/WEND), classic I/O (PRINT, INPUT), subroutines (GOSUB/RETURN), and essential console commands.
👉 It can be enjoyed as:
- 🎮 A toy environment for newcomers to play and learn programming basics.
- 📼 A retro playground for experienced BASIC programmers.
- 🧩 A compact codebase open to modifications, enhancements, experiments, and pure programming fun.
✨ Features
- ➕ Multi-statement lines using colon (
:) - 💬
REMcomments - 🔢 Numeric expressions and logical operators
- 🎲 Built-in functions:
RND(),CHR() - 🎨 Console control:
LOCATE,COLOR,CLS,WAIT,INKEY - 💾 File operations:
LOAD,SAVE - 🔠 Automatic uppercase conversion for keywords and variables
📖 Example
10 REM Guess My Secret Number - Super Tiny BASIC
20 CLS
30 COLOR 0, 7 : PRINT "Guess My Secret Number (1-100)"
40 LET A = RND() % 100 + 1
50 LET B = -1 : LET T = 0
60 WHILE B <> A
70 LET T = T + 1
80 COLOR 0,7 : PRINT "No of tries: ",T
90 INPUT "Enter your guess: ", B
100 IF B < A THEN COLOR 0,14 : PRINT "Too low!"
110 IF B > A THEN COLOR 0,12 : PRINT "Too high!"
120 WEND
130 PRINT "Congratulations! You guessed it: ", A, " in ", T, " tries!"
140 END📂 Full source code and example programs included in the EXAMPLES\TINY folder.
🎮 Demo Game
A full Hobby BASIC demo running inside the Windows 10 console.
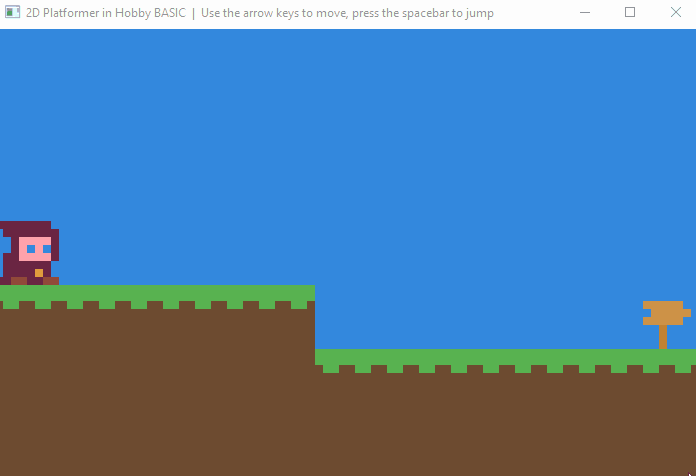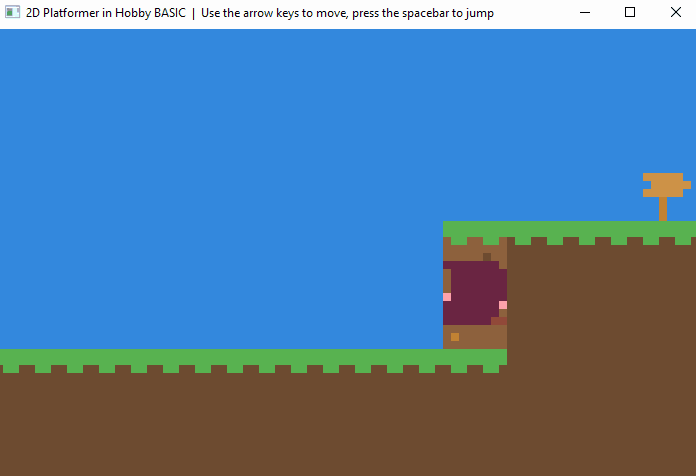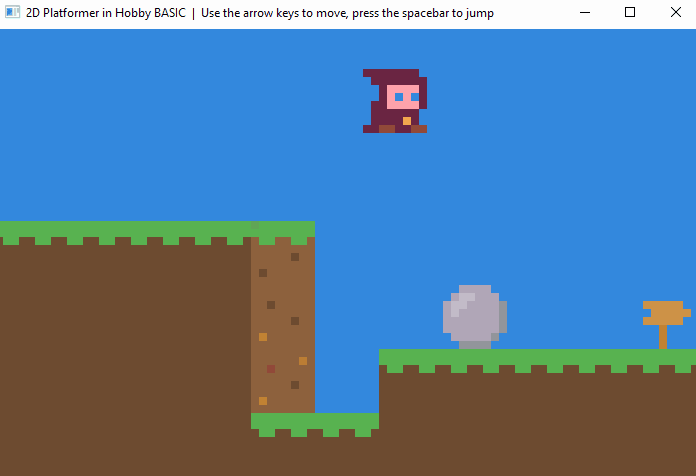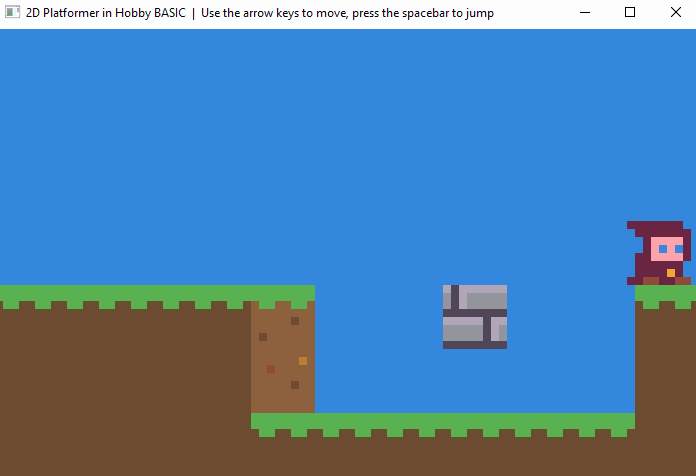
▶ View source code
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! DEMO.BAS
! Hobby BASIC Interpreter
! Example program from the Hobby BASIC collection.
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! DEMO DESCRIPTION
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
!
! 2D Platformer Demo with physics and multi-level progression.
! Jump, climb ladders, and navigate through 4 challenging levels.
! Features smooth character animation, collision detection, and gravity physics.
!
! Controls:
! - Arrow Keys: Move left/right and climb ladders
! - Space: Jump
! - ESC: Exit game
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! COMPATIBILITY NOTE
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
!
! For Windows 10/11:
! Enable "Use Legacy Console" in Properties for proper display
! (Right-click title bar → Properties → Options tab)
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! SYSTEM CONSTANTS AND INITIALIZATION
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FILE_OR_FOLDER_EXISTS = 3
MB_ICONERROR = 0x10
! System compatibility check
if VAL(PATH(6)) < 6
alert MB_ICONERROR, PATH(3), "Demo Requires Windows 7 or later" : end
endif
! Load graphics tileset
path_gfx$ = PATH("DATA\SNAP\TILESET.HB")
if FILE(path_gfx$, FILE_OR_FOLDER_EXISTS) = 0
alert MB_ICONERROR, "Tileset not found", path_gfx$ : end
endif
! Sound initialization
JUMP_SND = 700
sound PATH("DATA\MEDIA\SFX\WAV\SFX1.WAV"), JUMP_SND
! Virtual key codes for input handling
enum VK_LEFT=37, VK_UP, VK_RIGHT, VK_DOWN
VK_ESC = 27
VK_SPACE = 32
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! GAME CONSTANTS
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
FRAME_RIGHT = 7 ! Character sprite facing right
FRAME_LEFT = 17 ! Character sprite facing left (mirrored)
FRAME_CLIMB = 8 ! Character climbing sprite
TILE_SIZE = 8 ! Size of each tile in cells
JUMP_OFFSET = 12 ! Maximum jump height in cells
GAME_INTERVAL = 20 ! Frame time in milliseconds
level = 1 ! Current level (1-4)
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! COLOR PALETTE (16-color palette for the game)
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
dim rgb_color[] = \
0x000000, 0x584751, 0x49AB52, 0x3A4994, 0x3E628E, 0x43266B, 0x3381C1, 0xB8A7B0, \
0xA48E9A, 0xDE8833, 0x52B55A, 0x33A8F3, 0x304C6E, 0xACA2FF, 0x4892CE, 0xC9BBC2
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! LEVEL DESIGNS
! Tile IDs:
! 0 = Empty/background
! 1 = Solid ground
! 2 = Platform blocks
! 3 = Special block 1
! 4 = Ladder
! 5 = Ladder top
! 6 = Special block 2
! 9 = Level exit/goal
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
dim map1[11,7] = \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
1,1,1,1,1,2,2,2,2,2,9, \
0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1, \
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0
dim map2[11,7] = \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,9, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,5,1,1,1, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,4,0,0,0, \
1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,0,0,0, \
0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0
dim map3[11,7] = \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
1,1,1,1,5,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
0,0,0,0,4,2,2,6,2,2,9, \
0,0,0,0,4,2,1,1,1,1,1, \
0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0,0
dim map4[11,7] = \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2, \
2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,2,9, \
1,1,1,1,5,2,2,3,2,2,1, \
0,0,0,0,4,2,2,2,2,2,0, \
0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1,1,1,0
! Player starting positions for each level (tile coordinates: x, y)
dim hero_start_positions$[] = "00","03","04","02","03"
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! DISPLAY INITIALIZATION
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
title "🎮 2D Platformer Demo • Use ← ↑ →, Space to jump"
view 0, 7 ! Hide window, 8x8 pixel font
screen 80, 75, 0 ! Set console size
cursor 0 ! Hide cursor
color 0, 0 ! Black text on black background
cls ! Clear screen
! Load tileset graphics
snap 0, 0, path_gfx$
! Copy individual tiles from tileset to graphic slots
for i = 0 to 7
bsave i * 8, 0, TILE_SIZE, TILE_SIZE, i
next
! Special tiles (mirrored left-facing sprite and climbing)
flip 56,0,TILE_SIZE,TILE_SIZE,0 ! Create mirrored sprite
bsave 56,0,TILE_SIZE,TILE_SIZE,17 ! Store as left-facing frame
bsave 64,0,TILE_SIZE,TILE_SIZE,8 ! Climbing frame
bsave 72,0,TILE_SIZE,TILE_SIZE,9 ! Special tile
! Apply color palette to all 16 colors
for i = 0 to 15
rgb i, rgb_color[i]
next
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! GAME SUBROUTINES
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
! Update character position and sprite
! Parameters: x, y = character coordinates, frame = sprite frame to display
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub update_character(x, y, frame)
bloads x, y, frame
ends
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
! Check if character is on a ladder at given position
! Returns: 1 if on ladder, 0 otherwise
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub is_on_ladder(x, y)
for local i = 1 to TILE_SIZE - 1
cinfo x + i, y - 1
if V1 = 4 then rets 1 ! Color 4 = ladder
next
rets 0
ends
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
! Check if character should fall (no ground below)
! Returns: 1 if falling, 0 if on solid ground
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub check_falling()
for local i = 1 to TILE_SIZE - 1
cinfo x + i, y + TILE_SIZE
if MATCH(V1,1,7,8,10,12,15) then jumping = 0 : rets 0
next
rets 1
ends
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
! Check if character can move in horizontal direction
! Parameters: dx = direction (-1 for left, TILE_SIZE for right)
! Returns: 1 if movement allowed, 0 if blocked
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub can_move_horizontal(dx)
for local i = 0 to TILE_SIZE - 1
cinfo x + dx, y + i
if MATCH(V1,1,7,8,10,12,15) then rets 0
next
rets 1
ends
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
! Render the current level map to the screen
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub render_level_map()
for local y = 0 to map_height-1
for local x = 0 to map_width-1
bloads x * TILE_SIZE, y * TILE_SIZE, map[x, y]
next
next
ends
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! LEVEL SETUP AND INITIALIZATION
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
start#
view 0 ! Hide console window
! Level cycling (1-4)
if level > 4 then level = 1
! Get current map dimensions
map//level[].SIZE
map_width = V1
map_height = V2
! Create and copy level map
dim map[map_width, map_height]
map[].COPY map//level[]
! Calculate screen dimensions
ROWS = map_width * TILE_SIZE
COLS = map_height * TILE_SIZE
! Create background buffer
dim stage[ROWS, COLS]
! Set up graphics area
screen ROWS, COLS, 0
color 9, 9
paint TILE_SIZE, TILE_SIZE, ROWS, COLS, -1, -1
! Render level and capture to buffer
dir = 1 ! Start facing right
render_level_map()
grab 0, 0, ROWS, COLS, stage[], 0
! Initialize timing for frame rate control
lastGameTime = PEEK(0) & 0x7FFFFFFF
! Set player starting position
hero_start$ = hero_start_positions$[level]
tile_x = VAL(LEFT(hero_start$, 1))
tile_y = VAL(RIGHT(hero_start$, 1))
x = tile_x * TILE_SIZE
y = tile_y * TILE_SIZE
! Display character at starting position
update_character(x, y, FRAME_RIGHT)
view 1 ! Show console window
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! MAIN GAME LOOP
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
main#
! Frame rate control
currentTime = PEEK(0) & 0x7FFFFFFF
if currentTime - lastGameTime < GAME_INTERVAL
wait 1 ! Reduce CPU usage while waiting
goto main
endif
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
! JUMPING AND GRAVITY SYSTEM
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
if jumping
! Character is currently jumping upward
if y = JUMP_HEIGHT
jumping = 0 ! Reached jump peak
vy = 1 ! Start falling
endif
else
! Check if character should fall
vy = check_falling()
if vy = 0 then onGround = 1 else onGround = 0
endif
! Jump initiation (space bar while on ground or ladder)
if KEY(VK_SPACE) and (onGround or is_on_ladder(x, y))
sound JUMP_SND ! Play jump sound
jumping = 1
onGround = 0
JUMP_HEIGHT = y - JUMP_OFFSET ! Calculate jump peak
vy = -1 ! Start moving upward
endif
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
! LADDER CLIMBING
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
if KEY(VK_UP) and is_on_ladder(x, y)
! Continuous climbing while up key is pressed
while 1
if KEY(VK_UP)
grab x, y, TILE_SIZE, TILE_SIZE, stage[], x, y
y-- ! Move up one cell
update_character(x, y, FRAME_CLIMB)
wait 20 ! Climbing speed
elseif KEY(VK_DOWN) or not is_on_ladder(x, y + TILE_SIZE - 1)
break ! Stop climbing
endif
endw
endif
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
! HORIZONTAL MOVEMENT
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
if KEY(VK_LEFT) and can_move_horizontal(-1) and x > 0
dir = -1 ! Facing left
vx = -1 ! Moving left
elseif KEY(VK_RIGHT) and can_move_horizontal(TILE_SIZE)
! Check if reached level exit (right edge)
if x > ROWS - 10
level++ ! Advance to next level
goto start
endif
dir = 1 ! Facing right
vx = 1 ! Moving right
else
vx = 0 ! No horizontal movement
endif
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
! UPDATE CHARACTER POSITION AND DISPLAY
! ------------------------------------------------------------------------
if vx or vy or jumping
! Restore background at old position
grab x, y, TILE_SIZE, TILE_SIZE, stage[], x, y
! Update character coordinates
x += vx
y += vy
! Draw character with correct facing direction
if dir = -1
update_character(x, y, FRAME_LEFT)
else
update_character(x, y, FRAME_RIGHT)
endif
endif
! Update timing for next frame
lastGameTime = currentTime
! Continue unless ESC key is pressed
if not KEY(VK_ESC) then goto main
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! CLEAN EXIT
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
color 0,7 : cls ! Clear with black on white
view 11 ! 8x12 pixel font
end
🎨 P2P Drawing
Collaborative real-time drawing using UDP peer-to-peer networking running inside the Windows 10 console.
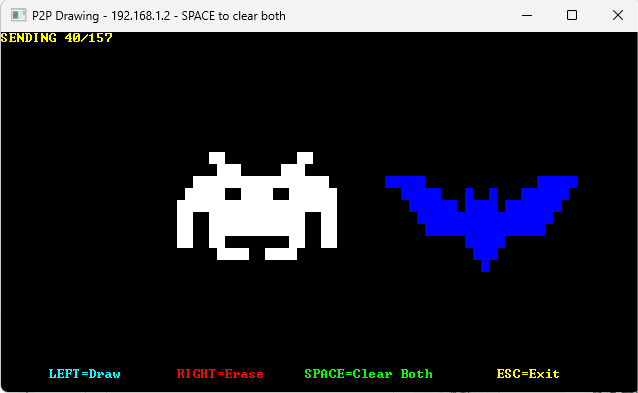
▶ View source code
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! P2PDRAW.BAS
! Hobby BASIC Interpreter
! Example program from the Hobby BASIC collection
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! APPLICATION DESCRIPTION
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
!
! Peer-to-peer collaborative drawing application using UDP sockets.
! Draw together with remote users in real-time - left click to paint,
! right click to erase. Press SPACE to clear both screens simultaneously.
!
! Controls:
! - Left Click: Draw/paint cell
! - Right Click: Clear/erase cell
! - SPACE: Clear both screens (synchronized)
! - ESC: Exit application
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! NETWORK FEATURES
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
!
! - Real-time drawing synchronization
! - Peer-to-peer UDP communication
! - Coordinate and color encoding
! - Synchronized screen clearing with feedback
! - Local network or localhost operation
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! --- Constants ---
VK_ESC = 27
VK_SPACE = 32
CMD_CLEAR$ = "P2PDRAW_CLEAR_SCREEN"
! --- Port configuration ---
enum PORT1=50002, PORT2
REMOTE_IP$ = "localhost"
LOCAL_PORT = PORT1
REMOTE_PORT = PORT2
! --- Open UDP socket ---
if OPEN(LOCAL_PORT) = -1
print "Socket error ", STR(V0) : pause : end
endif
! --- Mouse initialization ---
mouse() fix mouse : x = V0 : y = V1 : btn = V2
px = -1
py = -1
dim a$[10000]
! --- Screen setup ---
title "P2P Drawing - " + PATH(8) + " - SPACE to clear both"
view 11
screen 80, 30, 0
cursor 0
color 0, 0
cls
gosub RedrawControls
! --- Main loop ---
do
! --- SPACE: Synchronized clear ---
if KEY(VK_SPACE)
cls
gosub RedrawControls
pen 13
at 32, 12, "CLEARING..."
wait 250
SEND(REMOTE_IP$, REMOTE_PORT, CMD_CLEAR$)
at 32, 12, "SCREEN CLEARED!"
wait 250
at 32, 12, " "
pen 15
wait 250
endif
! --- Mouse drawing ---
n = 0
mouse()
if (btn = 1 or btn = 2)
c = IIF(btn = 2, 32, 0x2588)
pen 13 : at 0, 0, "DRAWING..."
do
mouse()
if (x <> px or y <> py)
pen 15
at x, y, CHR(c)
a$[n] = STR((((x << 7) | y) << 15) | c)
n++
px = x
py = y
endif
until btn = -1
at 0, 0, " "
! --- Send with progress feedback ---
if n > 0
pen 14
at 0, 0, "SENDING"
for i = 0 to n-1
SEND(REMOTE_IP$, REMOTE_PORT, a$[i])
pen 14
at 8, 0, STR(i+1) + "/" + STR(n)
wait 1
next
at 0, 0, " "
at 8, 0, " "
wait 10
endif
endif
! --- Handle incoming messages ---
while LEN(QUEUE(1))
msg$ = QUEUE(0)
if msg$ = CMD_CLEAR$
cls
gosub RedrawControls
pen 13
at 32, 12, "SCREEN CLEARED!"
wait 250
at 32, 12, " "
pen 15
else
n = VAL(msg$)
x = BITS(n, 28, 7)
y = BITS(n, 21, 7)
c = BITS(n, 14, 15)
pen 9
at x, y, CHR(c)
endif
endw
wait 1
until KEY(VK_ESC)
CLOSE()
end
RedrawControls#
locate 6, 28
pen 11 : print "LEFT=Draw ";
pen 12 : print "RIGHT=Erase ";
pen 10 : print "SPACE=Clear Both ";
pen 14 : print "ESC=Exit"
pen 15
return
🌐 Network Diagnostics
UDP and internet testing with visual DEBUG() output.
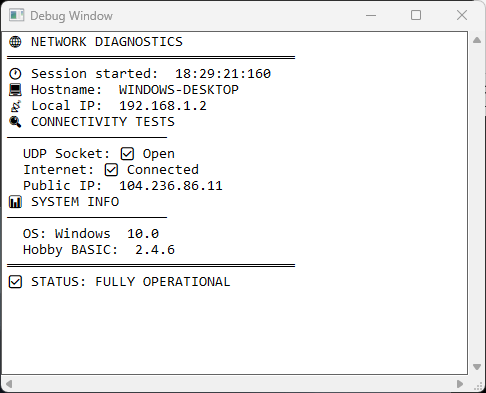
▶ View source code
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! NETWORK.BAS
! Hobby BASIC Interpreter
! Example program from the Hobby BASIC collection
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
! PROGRAM DESCRIPTION
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
!
! Complete network testing with DEBUG() window
!
! Features:
! - UDP socket connectivity testing
! - Internet access verification with public IP lookup
! - Visual feedback with emoji and color coding
! - System information display
! - Real-time status reporting in DEBUG() window
!
! ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DEBUG("CLEAR")
DEBUG("🌐 NETWORK DIAGNOSTICS")
DEBUG("════════════════════════════════════")
DEBUG("🕐 Session started: ", PATH(10))
DEBUG("💻 Hostname: ", PATH(7))
DEBUG("📡 Local IP: ", PATH(8))
DEBUG("🔍 CONNECTIVITY TESTS")
DEBUG("────────────────────")
socket_test = OPEN(0)
if socket_test <> -1
DEBUG(" UDP Socket: ✅ Open")
CLOSE()
else
DEBUG(" UDP Socket: ❌ Failed")
endif
public_ip$ = GETURL("https://api.ipify.org")
if LEN(public_ip$) > 0
DEBUG(" Internet: ✅ Connected")
DEBUG(" Public IP: ", public_ip$)
else
DEBUG(" Internet: ❌ No connection")
endif
DEBUG("📊 SYSTEM INFO")
DEBUG("────────────────────")
DEBUG(" OS: Windows ", PATH(6))
DEBUG(" Hobby BASIC: ", PATH(5))
DEBUG("════════════════════════════════════")
if socket_test <> -1 and LEN(public_ip$) > 0
DEBUG("✅ STATUS: FULLY OPERATIONAL")
else
DEBUG("⚠️ CHECK NETWORK SETTINGS")
endif
cls
print "Check DEBUG() window for network diagnostics"
inkey
end
📘 About Hobby BASIC
Hobby BASIC is a lightweight yet surprisingly powerful BASIC interpreter for the Windows console, written entirely in x86 assembly.
It enables the creation of games with ANSI graphics in the console, which is quite unusual.
What began in 2015 as a personal fun project continues to evolve to this day.
This quick guide offers just a small glimpse of what Hobby BASIC can do.
👉 To download it and learn more, visit the Hobby BASIC topic on the Flat Assembler forum.
👉 Watch a full video tour on YouTube to see Hobby BASIC in action.
Chrome may say: “This file is dangerous, so Chrome has blocked it.”
👉 Press CTRL + J and choose to Keep the file.
Windows Defender might also block it — you can:
- Temporarily disable real-time protection
- Add an exception after installing
Hobby BASIC started on Windows XP, continued on 7, and is now focused on Windows 10 and 11.
Some examples still work on older systems!
📌 Enable Legacy Console Mode
To ensure full compatibility with ANSI graphics and console behavior:
- Windows 10: Right-click the console title bar → Properties → Check "Use legacy console" → Restart the console
- Windows 11 (24H2 and newer):
- Go to Settings > System > Optional Features
- Click Add a feature and search for "Legacy Console"
- Install it, then go to Settings > Privacy & Security > For Developers → Change terminal to Windows Console Host
- Now open the console and enable "Use legacy console" as before
Don’t let system warnings discourage you. Experiment. Learn. That’s the spirit of hobby programming!
🔚 Conclusion
This guide covers the fundamental concepts of Hobby BASIC, from conditions and loops to functions and drawing tools. With this knowledge, you can start creating your own programs.